Section 3.2.1
In the Ancient Egypt for approx. 4500 years ago they had following lengths:
|
Lengths |
Metric system, meters |
|
1 Shet |
20.9440 |
|
1 Cubit |
0.5236 |
|
1 Remen |
0.3702 |
|
1 Foot |
0.2618 |
|
1 Hand* |
0.0740 |
|
1 Finger |
0.0185 |
Section 3.2.2
The correlation between the Ancient lengths are:
|
Shet |
Cubit |
Remen |
Foot |
Hand* |
Finger |
|
1 |
40 |
56 |
80 |
280 |
1120 |
|
|
1 |
√2 or 1.4142 |
2 |
7 |
28 |
|
|
|
1 |
√2 or 1.4142 |
5 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
3.5 |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Please observe the different factors:
· 1 Khet = 100 Cubits
· 1 Shet = 40 Cubits
· 1 Cubit = √2 Remen, 1 Remen = √2 Foot
· 1 Cubit = 2 Foots
· 1 Cubit = 7 Hands*
· 1 Hand = 4 Fingers ( 2 x 2 )
· 1 Foot = 14 Fingers ( 7 x 2 )
· 1 Cubit = 28 Fingers ( 7 x 2 x 2 )
· 1 Shet = 56 Remens ( 7 x 2 x 2 x 2 )
· 1 Remen = 5 Hands*
* Some sources call the length "hand" for a "palm", it is exactly the same size. I prefer to use the word "hand".
Section 3.2.3
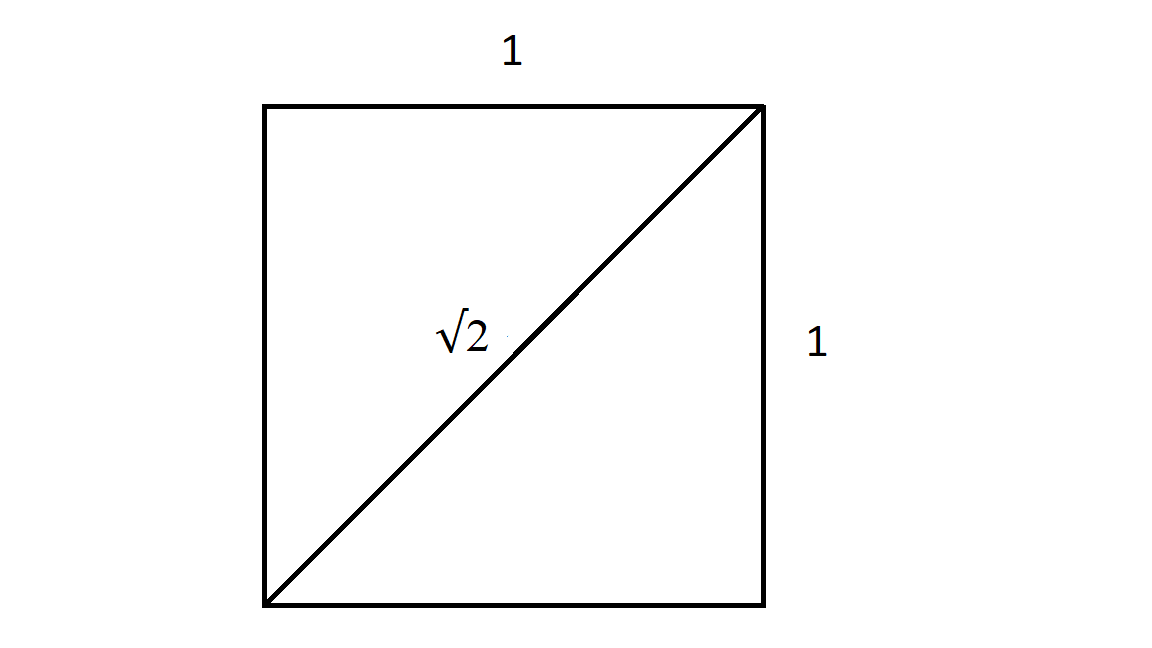
Square root of 2
Section 3.2.4
If a square measure 1 x 1, then the diagonal length
(the hypotenuse) is √2.
1. Cubit
2. Remen
If the above right triangle had two legs of 1 remen each then the hypotenuse is √2 remens = 1,414213562 remens, a number which was totally unknown in ancient Egypt.
Instead they defined that length as 1 cubit, so √2 remens = 1 cubit.
Section 3.2.5
Other measures
Area:
1 Setat = 1 square Khet
Section 3.2.6
Pi:
Pi (π) is a mathematical constant defined as the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
There is no evidence that the ancient Egyptians knew or used the
irrational number Pi (=
3.14159265359
or fractions like 22/7). They did not even
need it, when they calculated the measures inside and outside the pyramid.
The ratio between the circumference of a circle and its diameter of 1 cubit was defined as 6 cubits, (which is 3,14160 calculated in the metric system).
They used fractions in general as 1/x, x is ( x = 2,3,4,5 ...) - exception is the fraction 2/3.
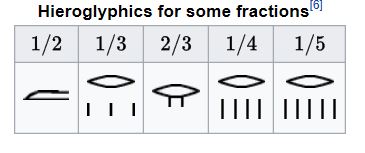
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ancient_Egyptian_mathematics
Section 3.2.7
Volume:
1 Hekat = 4,8 litres
1 Hin = 0,48 litres
Section 3.2.8
Angle or slope:
The ancient Egyptians did not calculate angles. They calculated the decrease or increase of steepness.
1 Seked = The horizontal length measured in hands / The vertically length measured in cubits.
The slope of the Khufu pyramid is 5 1/2 sekeds calculated as:
220 cubits horizontally x 7 hands/cubits / 280 cubits vertically = 5 1/2 sekeds.
There is a connection between a seked and an angle.
Imagine a right triangle with each side of 1 cubit as an example:

The horizontal is 1 cubit equal to 7 hands.
7 hands horizontal / 1 cubit vertical = 7 seked which is an angle of 45°
In general we can deduct following:
The cotangent to the angle is the adjacent side / the opposite side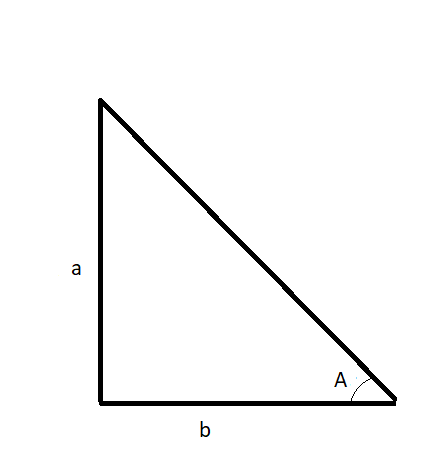
then
if
then
or
and the angle A is:
Section 3.2.9
I have developed this tool in Excel, if you need a copy of the Excel sheet, please write to me to stefan.a.h.holmgren@gmail.com